Solar PV guide

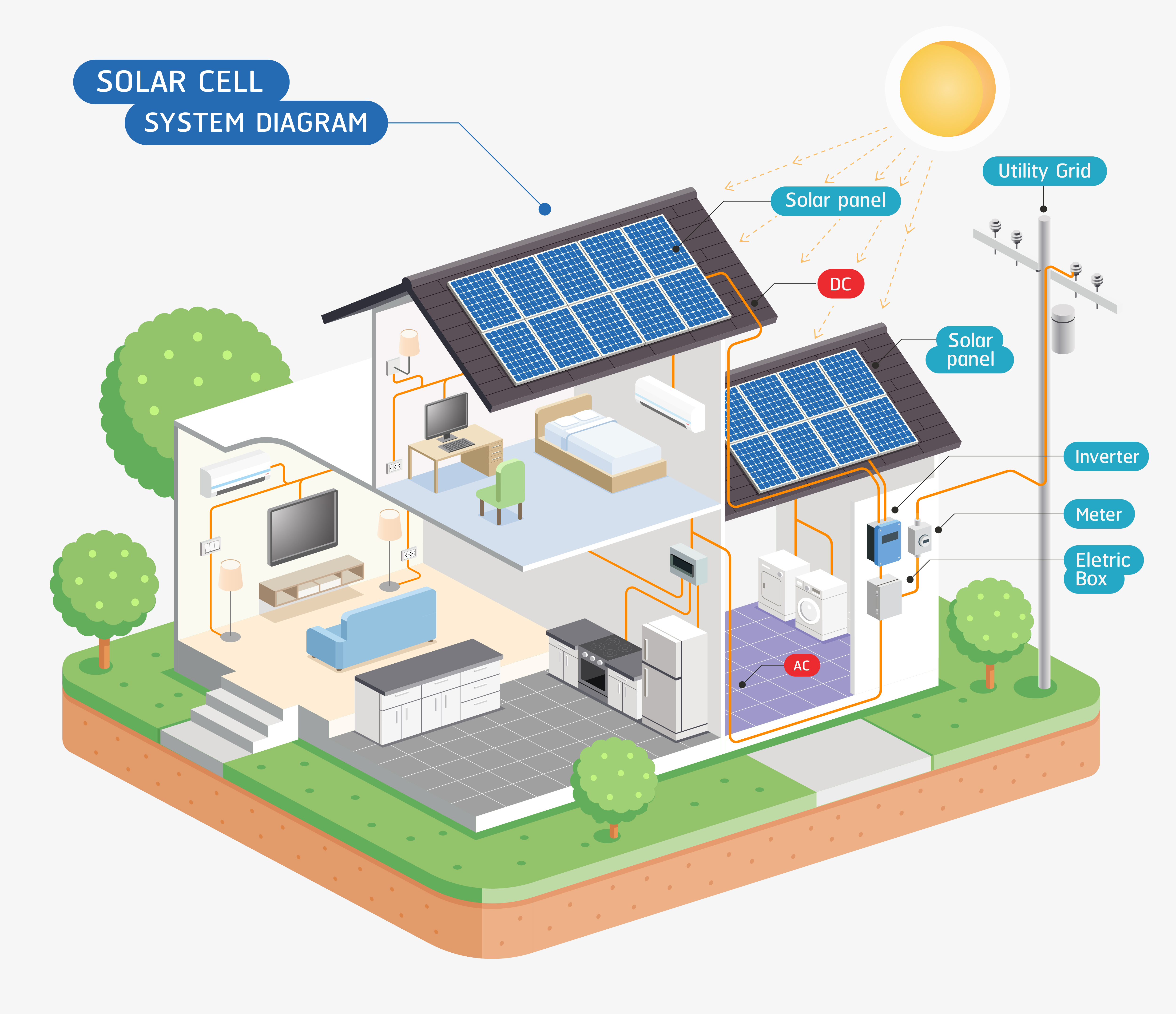
Solar PV stands for Solar Photovoltaics, which is when light is converted into electricity. Sunlight is absorbed by the solar panels, which generates DC electricity. This goes through the inverter which converts it into AC electricity.
Connected to the inverter is the consumer unit (fuse board) which allows the electricity to be used within the property.
PV cells are used in the solar PV system to collect sunlight and convert it into electricity. The cell is made up of one or two layers of semi conducting material and once sunlight is shone onto them, an electric field is created across the layers which creates electricity. The more sunlight, the more electricity.
PV cells are referred to in kWp (kilowatt peak) which is the amount of energy that is generated in full sunlight.
A solar PV system is typically made up of the following components:
Solar photovoltaic panels
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels (sometimes called modules) are units made up of cells that create an electric field when the sun shines onto them. When the sun is strong, more electric is generated however, electricity can still be produced on a cloudy day.
When there are a few PV panels (modules) wired in a series, this is called a string. The operating voltage of the system is determined by the string.
The Array is the result from the formation of the cell, the modules and the string.
The Inverter
The inverter is a very important part of the solar PV system as this is the component that converts the direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Power that is generated from the array, is converted by the inverter and then connected via isolators (one on the DC side and one on the AC side) into the consumer unit.
Generation meter
The generation meter allows you to monitor how much energy your solar PV system is generating. The stronger the sun, the faster the flashes of the red light on the meter will be.
Export limiters
The export limiter is a component that is not always installed. When it is, it is installed next to the consumer unit.
These are installed when excess electricity has been generated. The excess would normally be exported to the grid however if your District Network Operator declines this, the export limiter will cap or stop the exportation.
Energy monitoring
To ensure correct system operation, it is good practise to monitor the system. Making a note of the output of the solar PV system once a month & making a comparison to the expected output will allow you to see if there are any differences. If it is not performing how you would expect, this would need to be investigated by our team.