Ground source heat pump guide
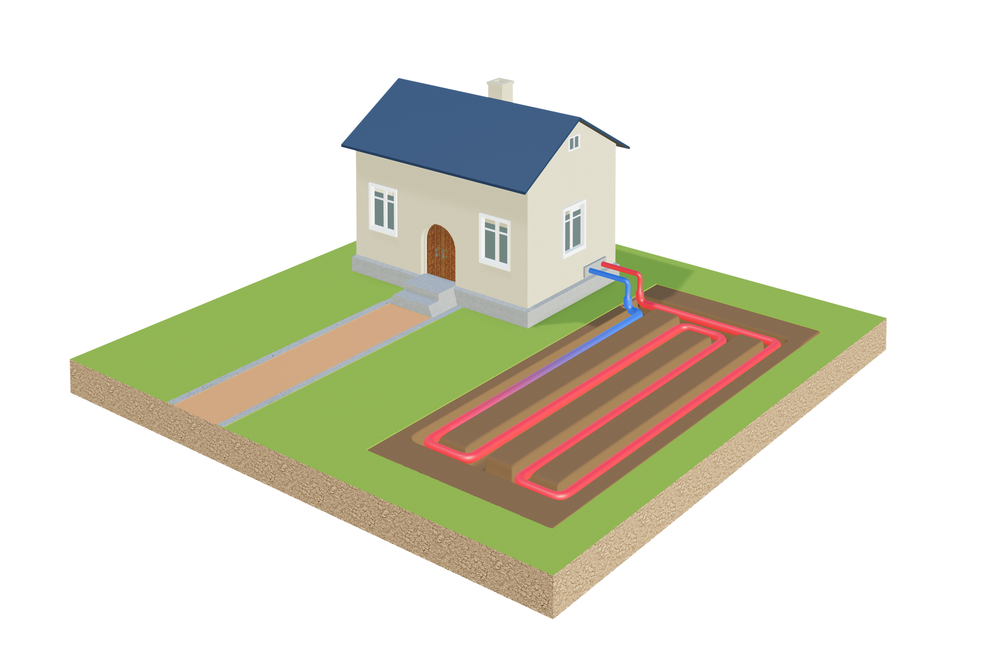
Ground source heat pumps work by taking heat (thermal energy) from the ground outside and converting this into hot water and heating for the property. These type of heat pumps work in cold temperatures and are for properties with suitable land for installation of ground arrays or a borehole system.
Electricity is required to operate these heat pumps however only 25% of usage will be electricity whilst the other 75% will be energy generated from the ground – emissions are therefore reduced.
Ground array
A ground array is pipes that are installed underground. The heat (thermal energy) is absorbed by the pipes from the ground and then converted by the heat pump to heating and hot water.
Digging machinery will be required to dig trenches so a larger space of land will be required. Although the initial installation requires a lot of space, once complete, it will not be noticeable.
Borehole system
Borehole systems are used in place of ground arrays for properties that have smaller land space.
A borehole is a hole that is dug deep into the earth to reach the heat (thermal energy). The deeper the hole is, the more heat (thermal energy) can be absorbed. Borehole depths vary depending on the property.
Installation time is usually quicker than ground arrays however digging and drilling machinery will still be required.
Once installation is complete, the system will not be noticeable.
Advantages of ground source heat pumps
- Heating and hot water source for your property
- Great for properties with land
- Works for a range of properties
- Quiet whilst running
- Works with current or new radiators and underfloor heating
- Heat pumps can sit inside or outside
- Maintenance is minimal
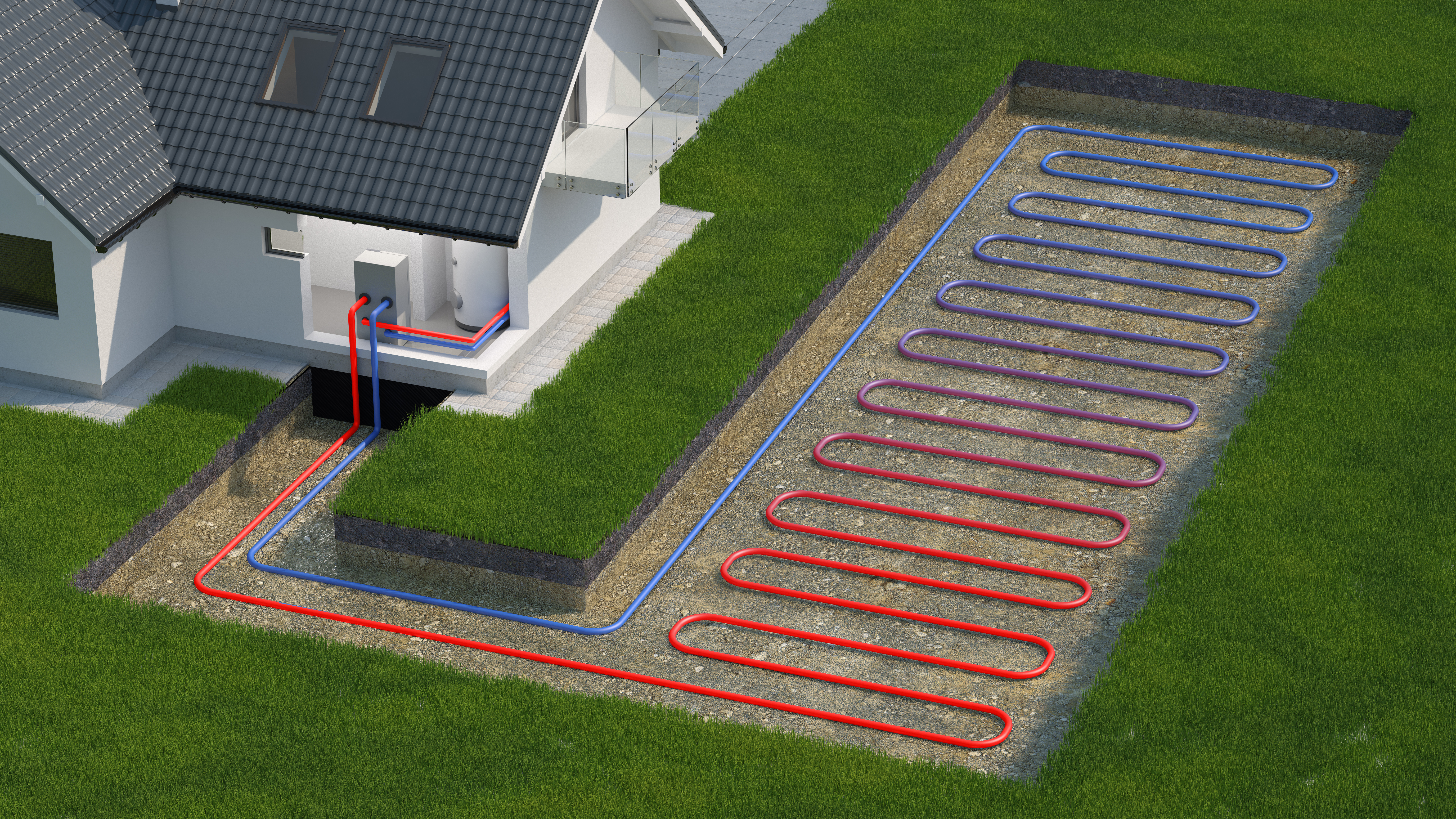
If you have any questions about ground source heat pumps, please do not hesitate to get in touch. Our qualified engineers will be able to advise if your home is suitable.